The common or general tactical surprise is that which is normally or frequently used and that is known and expected. There is one case we take as example, which is to ambush or hostilize enemy forces who come to help or rescue a group of their own immobilized and/or besieged by us. This attack is logical to do so, because the forces in march, and especially when the urgency drives them, are especially vulnerable: because of the weakness of their flanks, for their scant reconnaisance and greater ignorance of their marching grund to combat, and for their deployment or marching column more or less frayed.
The attack is to be made using sequential or simultaneously different techniques: ambushes, even employing small units; free shooters lines; shutts of the advance routes and his wings with mines; bombardments of the artillery and the unit’s organic mortars, using registered fire on the routes or its singular points; attacks of the own or allied aviation; appearances and assaults by an our «combat group» (of combined arms?) in his immediate rear or covering it in a flank of the itinerary that is favorable for our protection (heights line, edge of forests, industrial and urban areas).
It is necessary to use necessarily this common surprise. But, the attacker must not repeat his set of tactics and military technics during short periods of time. In order that our attack is not so predictable, also in the details and manners, which facilitates his rejection to the enemy. Since with our routine, we are announcing the enemy which is our game, showing him the cards. And, let’s know that, even with these precautions, we are teaching him to fight.
With the mentioned variety, his combinations and the opportunity of use, the enemy will not be able to take sufficient measurements for the rejection. Since the variants of action that we can use are sufficiently different and numerous.
This is a tactical surprise, in the same level in which we are unrolling ourselves. That will allow us to increase the attrition (on the means) and the wear (of the men) of the enemy. And, even, to place and move more favorably with regard to him. But the total results will depend on the development of the set of the raised operations. Based on the forms of fight, the movements and the involved men and means.
 Colonel General Walther Model.
Colonel General Walther Model.
This way, this surprise less elaborated conceptually produces fewer fruits that have operational or decisive transcendency. Everything indicates that, in order that it should take place and increases qualitatively the transcendent efficiency in our actions, it is necessary that the quality of the surprise reaches another dimension in his action.
It is necessary, so, in the operational level of the surprise, that this would be an «ungrateful surprise» for the enemy. That has catastrophic effects, though they are local, on him, at the beginning. And that the «commotion waves» in the area or the affected sections, propagate for the enemy military system attacked. Damaging his capacities, his general and grupal moral (a section, the fighters of a weapon) and his intentions and perspectives. It would be equivalent, in the raised scene, to an «exploitation of the success» of our actions. That are encouraged and perfected by the operational surprise obtained.
The following battle during World War II illustrates the use of unexpected «field of action» on the enemy, and the use of ordinary and heterodox forces. That allowed General Walther Model to take the initiative and destroy a Soviet army inserted in his operational rear.
During the winter counter-offensive of 1941-1942, the Soviet Union military had penetrated the operational rear of the 9th German army of Colonel General Model. It was integrated in the Central Armies Group, under the command of Fieldmarshal von Kluge. The Germans withdrew to positions near populated areas, tacked between them by its artillery fire and keeping open a few, precarious communications lines between the units. Thus helping maintain the operational stability of the army’s defensive area.
The Soviets had crossed the lines of the semi-continuous front, crushing weak German positions and setting up in the german rearwarsd the 39th infantry army and the XI cavalry corps (mobile forces for areas of difficult ongoing), a total of 60,000 men. Their deployment was protected in the semi wild forests and marshes between Boly and Rzhev, the principal regional city, and was supplied by a route that edged by Boly and continued to Nelidovo at the north of the zone. These Soviet forces were also in operational hibernation, waiting for the late thaw of the Russian spring.
This powerful enemy nucleus, in coordinated action with Soviet forces at the front, could compromise the German summer offensive (1942) by cutting the supply lines of the 9th army. For this reason, it was necessary to liquidate it before tackling a new campaign.
Under the instructions of General Model, a movil force was put together. This formed a hippomobile brigade with the reconnaisssance forces (a reduced battalion) of each eight divisions of infantry of 9th army, all of which had all ground transit capacity.
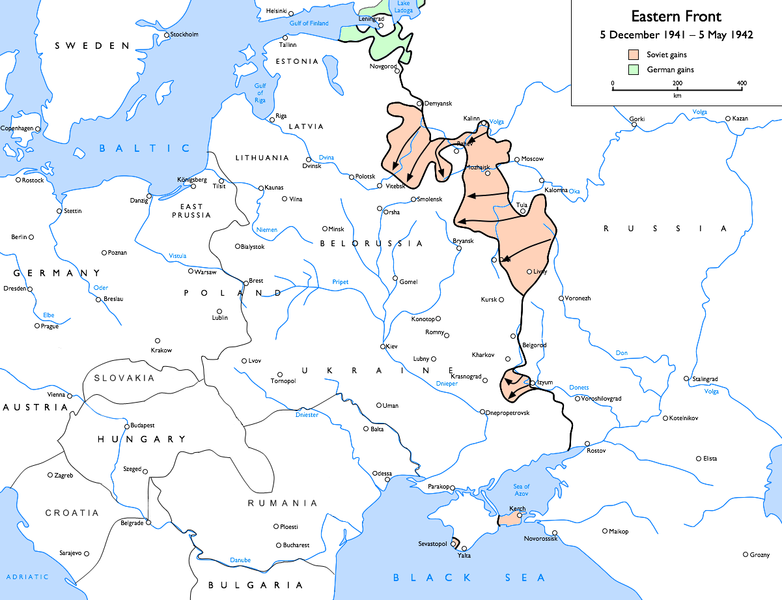 The Rzhev’s projection was formed after the Soviet counter-offensive in defense of Moscow.
The Rzhev’s projection was formed after the Soviet counter-offensive in defense of Moscow.
The mission of this brigade was to slip through enemy flanking sectors not covered by the security and principal positions of the enemy. Once in enemy territory, they were to wait for a principal important attack, to begin fighting in the enemy’s interior with the hope of occupying defense nucleus positions. The German aim was to severely unsettle the Soviets’ deployment and the conduction of their defense plan.
By using its forces in the unexpected «field of action«, the Germans hoped to recover the freedom of action to impose on the enemy the law of the action. The objective was simple, but its attainment was difficult.
The brigade, which was to penetrate the Soviet zone, was led by the 5th panzer division of Major General Gustav Fehn. That were the principal interarms forces and the mass of support or normal forces. They were to proceed following the principal reinforced surface road of the zone. Which passed from Olenino in the north and followed the western slope of the Luchesa river.
Soviet troops (39th infantry army), inside its defense zone clung to this road and had an antitank deployment (obstacles and guns). The Soviet flanks were thin but protected on each side by extensive minefields. Its right flank rested on the inhospitable and impassable woods and swamp lands of the deep valley of the Luchesa which, in the Soviets’ thinking, protected them against serious attack. The Soviet command foresaw what must be the German’s principal effort against them and deployed their forces with creativity and inventiveness.
Only healthy, strong, veteran soldiers who worked well together and whose units had cohesion could be used in this mission. It was not work for garrison troops brought from the German rear or the occupied countries. Because of this, Walther Model did not hesitate to deprive his infantry divisions of its only mobile units of maneuver to use in this battle.