THE SECOND TRANSFORMATION
FIRST HALF VIII CENTURY TO BEGINNING XII CENTURY
The salafist Ideology.
Salafism, from «salaf«, predecessor or ancestor, is the other ideological school of the Islam. As salaf, the Muslims call Mohammed and his disciples: the first four caliphs and the next two generations. The expansion of the Islam in the 7th century assumes to the purity of his faith. Since this brought them the Allah’s favor and support.
Since then, whenever the Moslem societies are sufering an economic, political or social crisis, prominent figures will arise that will praise a return to the Islam of the Salaf. Ibn Hanbal, in the 9th century, gives a literal interpretation of the Islam, based in recovering the ancestors and in the condemnation to the ideological innovations. Ibn Taymiyya resorted equally to her in the 14th century, when the Middle East was suffering the Mongolians invasions. These would be the initiators of this current or school.

The salafist currents are renaissance movements of the Islam, through the return to the original faith, that of the «pious predecessors«. They reject everything that identify as «human interpretations after the revelation of the Prophet«. They are radical reformists movements, which condemn the practices of the «popular Islam« (accused of being superstitions) and great part of the ideological Moslem thought, considered as carrier of «innovations». That is to say, «creations of the human reason«, that move away from the divine message. The salafists reject in turn the influence of the Western civilization, particularly the democracy, the relativism and the laity, that «corrupt the Moslem faith«.
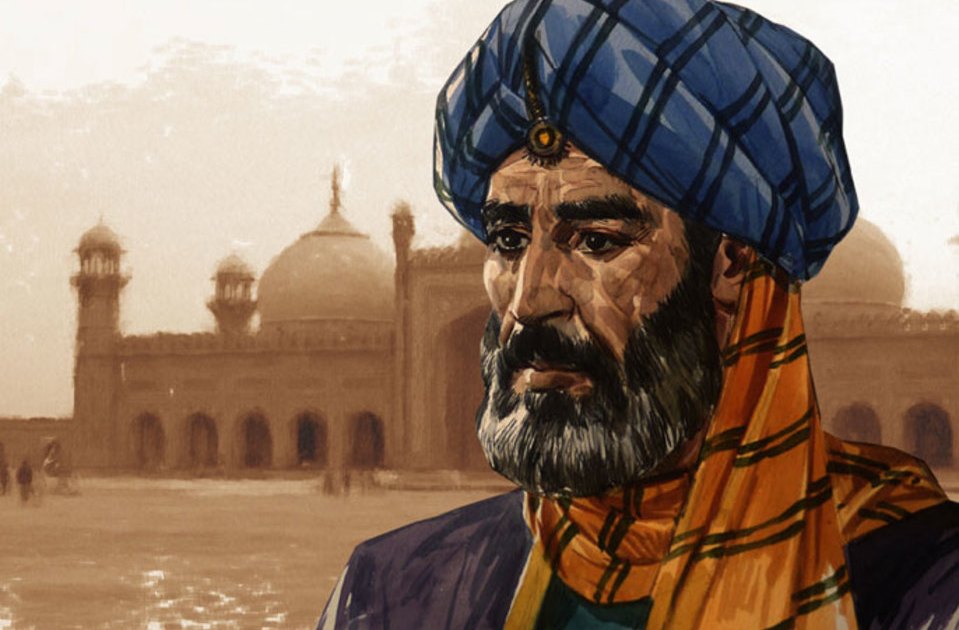

The salafists become emancipated of the tradition founded by the 3 sunnis canonical schools. And they invent another Islam, which they affirm is founded on the Coran and the Sunna. Also they seek to imitate Mohammed in all the acts of the daily life, included the way of eating or dressing.
The wahhabism or the salafism at the political Power.
The modern salafists begin with the preaching of the Arabic ulema Mohamed Ibn Abdul Wahhab (1703-1792). Who thought that the decline of the Moslem countries opposite to the West, ensues from the oblivion of the original message of the Islam. Ibn Abdul Wahhab preaches the literal and puritanical reading of the Islam, following the Hanbalist and Ibn Taymiyya traditions. Searching for «the correct way of acting in the teachings of the pious predecessors». His sermons were not well received and was expelled from his natal locality, in the Nejd region. He went to Diriyah’s city and there formed an alliance with the sheikh Mohamed ibn Saud, founder of Saud’s House. Ibn Saud promulgated the idea of the «wahhabí» Islam as the official way of practising the Islam in the country. For his part, al-Wahhab gave the religious legitimacy to Ibn Saud in his conquest of Arabia.

Finally, in 1902, the emir Abdul Aziz ibn Saud reconquered Riyadh. In 1924 occupied Mecca and Medina and in 1932, all the Saudi Arabia. This was giving them the control on the Hajj, the annual pilgrimage to the Muslim Sacred Places and the opportunity to preach the wahhabism to the pilgrims from all the countries. But, the wahhabism was a minor current of the Islam until 1938, when the oil reserves were discovered in the zone. The immense incomes from this new wealth gave a great impetus to his ideological expansion for the world.
The imans near to the Saudi regime, reject the jihadist way, that tries to impose a Moslem regime by means of the violent and revolutionary action. On having considered it to be condemned to the failure. One of his great figures, from the 60s up to his death in 1999, the sheikh Mohamed Nasiruddin al-Alabani, was declaring that «nowadays, it forms part of the good politic, to leave the politic». For al-Albani it was necessary to follow a strategy of purification of the education: on one hand, to regenerate the faith, purifying it of ideological «innovations», that remove it from his origins; and to educate the Muslims in this regenerated faith, in order that they leave his religious «corrupt» practices.

The «Jihadist salafism» or Qutbism.
This current of the school makes the Jihad one of his activity centers. The jihadism seek to accelerate the liberation of the Moslem countries of any foreign occupation. It is based on Sayyid Qutb’s ideas, a theoretic and revolutionary born within the Moslem Brothers. He was sure that the Western Society was sick with individualism and ungodliness. And the Moslem countries would suffer the same thing, if they were influenced by West. And affirmed that the actual Moslem regimes were apostates, on having applied lay laws, instead of the Sharia.

Qutb‘s thought was one of the principal influences in the sects Muslims’ Society or Excommunnication (takfir) and Hegira (migration), arisen in 1969 in the bosom of the Moslem Brothers in Egypt, and in al-Qaeda, and his leaders, Ayman al-Zawahiri and Osama Ben Laden. Sayyid Qutb, was detained, judged and executed at August 29, 1966, for planning the murder of the president Nasser. After his death, the Muslims Brothers evolved towards organization and fight forms inside the existing political system.
The actual salafist jihadism is born in the 80s, during the Afghanistan’s war against the Soviet occupation. The salafists jihadists arrived from Saudi Arabia met the Moslem Brothers. It drove them to adopt the political speech of the Moslem Brothers and to restoring in it the salafistst preaching of Sayyid Qutb.
Epilogue.
The practice praised by the salafistas introduced a strong ingredient of instability and of violence, still physical, between the Muslims and, therefore, between their ideological schools. That was depending and was a function of the antagonistic contradictions (insoluble in a pacific synthesis) that in every historical stage were generating and appearing in the Umma or in located parts of her and in the borders with the hostile peoples. The practical result was that the armed way became consubstantial and intermittently, in the mean of defense and spread of the Faith for many Muslims.
And though only a minimal percentage supports her nowadays and still they are less those who apply it, this conduct, as the red of the blood, turns out to be showy before all the men. That by extension and ignorance, attribute it to the totality of the Moslem community or Umma.
In addition, the sword is an enemy of the pen and of the abstract or scientific ideas. Or, at least, it fades and suffocates them. Though Mohammed already warned it in a hadis: «The ink of the pens is sometimes more useful for the Umma that the blood of the martyrs». At about the 5th century of the Hegira, our 11th century, the ideologists, in a political decision, closed the door to the ichtihad. And the methodological Islamic approach altered. From then, it was imitated, it was repeating itself, it was abused with the compendiums. There got lost the curiosity, the scientific personal effort, the flexibility, the intercommunication of studies and results. And, finally, since it could not be less, this ideological crystallization, moved also to the Moslem arts and sciences, that started a long declining.
This way, this second Transformation of the Islam remained largely frustrated and faded. By the new outcrop of the «minor Yihad», which constituted the first Transformation of the Islam. And that turned out to be completed and profitable with the incredible extension of the Islam in the known world in something more that one century. This reappearance of the first Transformation of the Islam, which was the use of the force for the extension and the implantation of a monotheistic religion, would turn into a complex, multiple, repetitive and violent action throughout the following centuries. Creating effusions of blood and spreading stertors of childbirth for different and numerous countries. On having searched with a new birth of the first Transformation of the Islam, the solution of the inevitable crises (for being vicissitudes of the personal and colectives lives) of the Muslims with the unfaithfuls or their chiies separated brothers…
Creating a permanent civil war, with a rosary of truces, within Islam, within the Umma, between Shiites and Sunnis.




 IMAM ABU HANAFI
IMAM ABU HANAFI
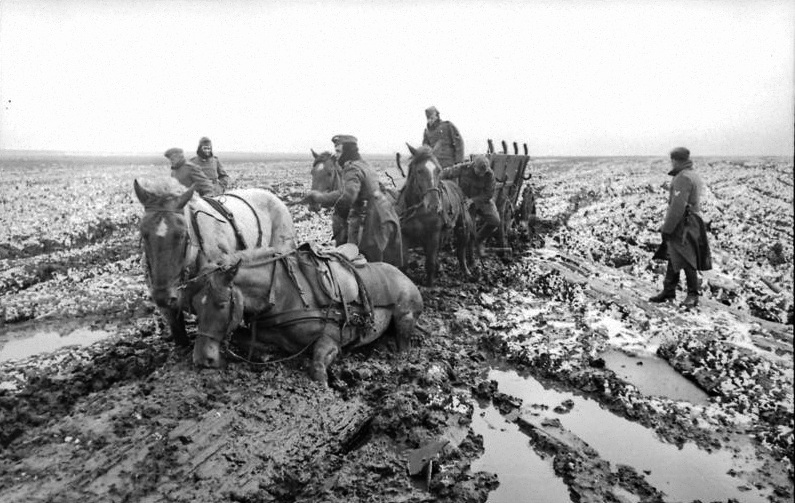
 Country wagons moving forward in a huge Russian plain…
Country wagons moving forward in a huge Russian plain…
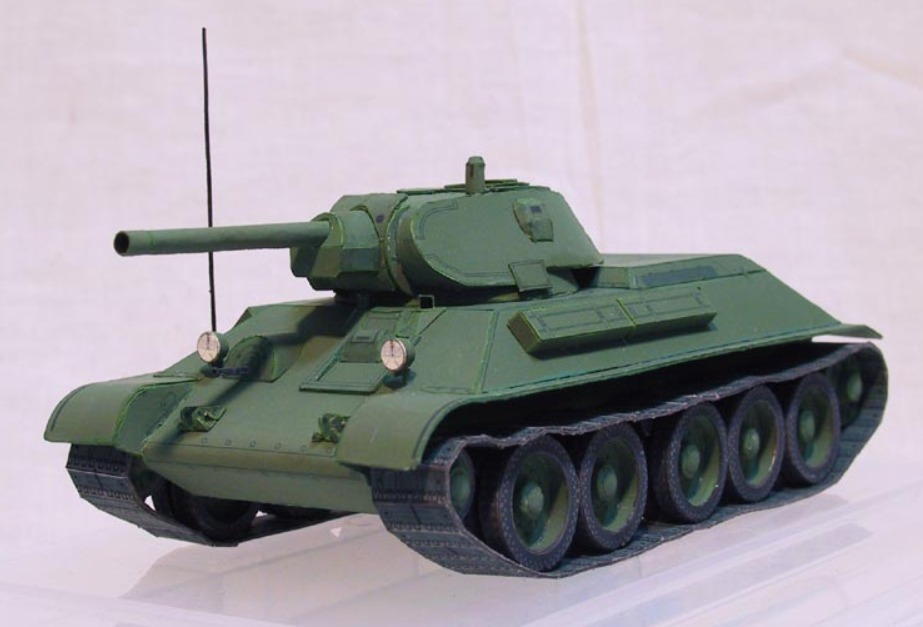

 A Panther from the 11th panzer division circa summer 1943
A Panther from the 11th panzer division circa summer 1943 Colonel General Walther Model.
Colonel General Walther Model.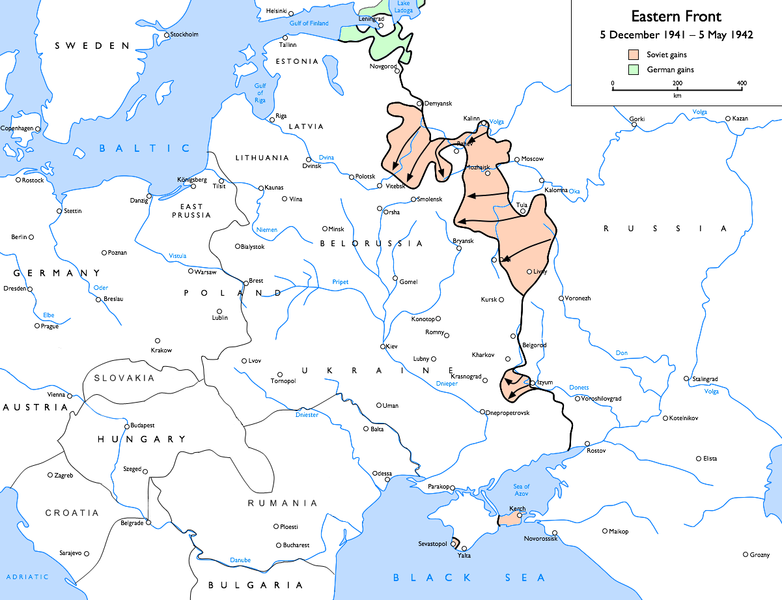 The Rzhev’s projection was formed after the Soviet counter-offensive in defense of Moscow.
The Rzhev’s projection was formed after the Soviet counter-offensive in defense of Moscow. FIGHTING ON THE BRIDGE.
FIGHTING ON THE BRIDGE. MONGOL’S LIGHT AND HEAVY CAVALRIES.
MONGOL’S LIGHT AND HEAVY CAVALRIES.

 BATTLE OF LIEGNITZ
BATTLE OF LIEGNITZ

 THE SOVIET POLISH WAR OF 1920.
THE SOVIET POLISH WAR OF 1920. SWEEPING THE RUSSIAN HORDES.
SWEEPING THE RUSSIAN HORDES. Soviet infantry tanks riders.
Soviet infantry tanks riders.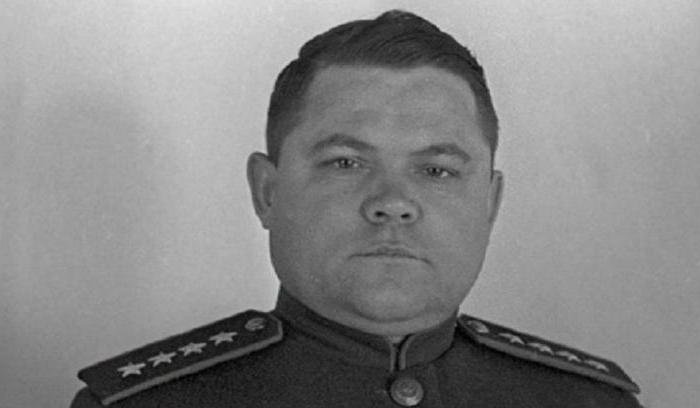 Lieutenant General Nikolai Vatutin, chief of the Southwest Front.
Lieutenant General Nikolai Vatutin, chief of the Southwest Front. Major General Vasily Badanov.
Major General Vasily Badanov. Fieldmarshall Erich von Manstein.
Fieldmarshall Erich von Manstein. Karl Spang, as German general.
Karl Spang, as German general. Lieutenant General Martin Fiebig
Lieutenant General Martin Fiebig T-70 Russian light tank.
T-70 Russian light tank. Colonel General Pavel Romistrov, commander of the 5º Tank Army of the Guard.
Colonel General Pavel Romistrov, commander of the 5º Tank Army of the Guard. Telegram of condolence of the General Assistant of the Secretary of the War to the family of one of the «missing persons» of the «Task Force Baum».
Telegram of condolence of the General Assistant of the Secretary of the War to the family of one of the «missing persons» of the «Task Force Baum».  Recent Marshal von Paulus surrenders his Staff in Stalingrad.
Recent Marshal von Paulus surrenders his Staff in Stalingrad. Colonel General of the Luftwaffe Wolfram von Richthofen.
Colonel General of the Luftwaffe Wolfram von Richthofen. The Marshal of the USSR Aleksander Vasilievsky.
The Marshal of the USSR Aleksander Vasilievsky.




 GOOD AGAINST A II GENERATION ARMY AND MORE CENTRALIZED THAT OURS: THAT OF SADAM HUSSEIN.
GOOD AGAINST A II GENERATION ARMY AND MORE CENTRALIZED THAT OURS: THAT OF SADAM HUSSEIN. OBAMA FIRED CENTCOM GENERAL MATTIS WITHOUT A PHONE CALL.
OBAMA FIRED CENTCOM GENERAL MATTIS WITHOUT A PHONE CALL. SOME DEADLY RECORDS.
SOME DEADLY RECORDS. AGUSTÍN DE FOXA.
AGUSTÍN DE FOXA. DOES HE LOVE HIM MORE THAN THE SYRIAN PEOPLE?
DOES HE LOVE HIM MORE THAN THE SYRIAN PEOPLE?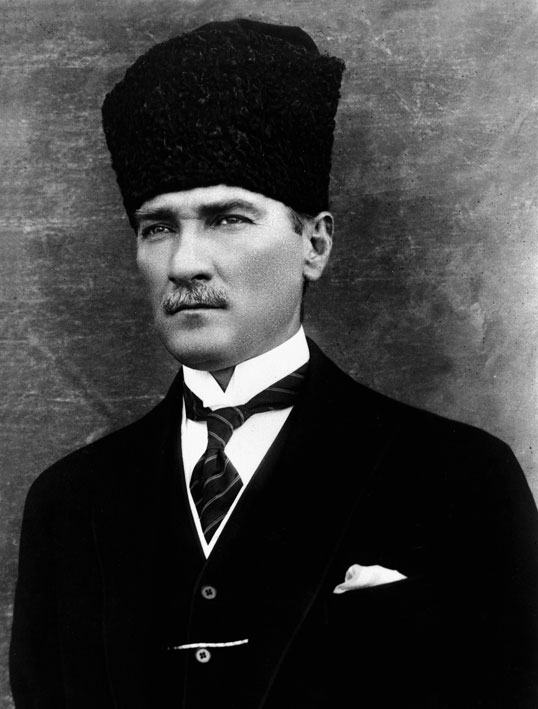 HE GAVE DESTINATION AND PRIDE TO HIS PEOPLE, DEFEATED IN THE FIRST WORLD WAR. WHERE THE MISTAKES OF THE SULTANATE (CALIPHATE) TOOK HIM .
HE GAVE DESTINATION AND PRIDE TO HIS PEOPLE, DEFEATED IN THE FIRST WORLD WAR. WHERE THE MISTAKES OF THE SULTANATE (CALIPHATE) TOOK HIM .  ALI KHAMENEI CALLED HIM: «LIVING MARTYR» OF THE IRANIAN REVOLUTION.
ALI KHAMENEI CALLED HIM: «LIVING MARTYR» OF THE IRANIAN REVOLUTION.
 COLONEL JOHN BOYD, AN AMERICAN TEORIST OF ITS MANEUVER THEORY.
COLONEL JOHN BOYD, AN AMERICAN TEORIST OF ITS MANEUVER THEORY.  WILLIAM LIND, A CIVIL TEORIST.
WILLIAM LIND, A CIVIL TEORIST. GENERAL DONN STARRY, HIGH COMMAND OF THE U.S. ARMY’S TRADOC.
GENERAL DONN STARRY, HIGH COMMAND OF THE U.S. ARMY’S TRADOC.  KIM IL SUNG, THE FOUNDER OF THE DYNASTY.
KIM IL SUNG, THE FOUNDER OF THE DYNASTY.

 ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT IN CHINA.
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT IN CHINA. A FORMER NATIONAL DEFENSE COUNCIL…
A FORMER NATIONAL DEFENSE COUNCIL…
 SYRIAN SOLDIERS SALUTE TO CAMERA.
SYRIAN SOLDIERS SALUTE TO CAMERA.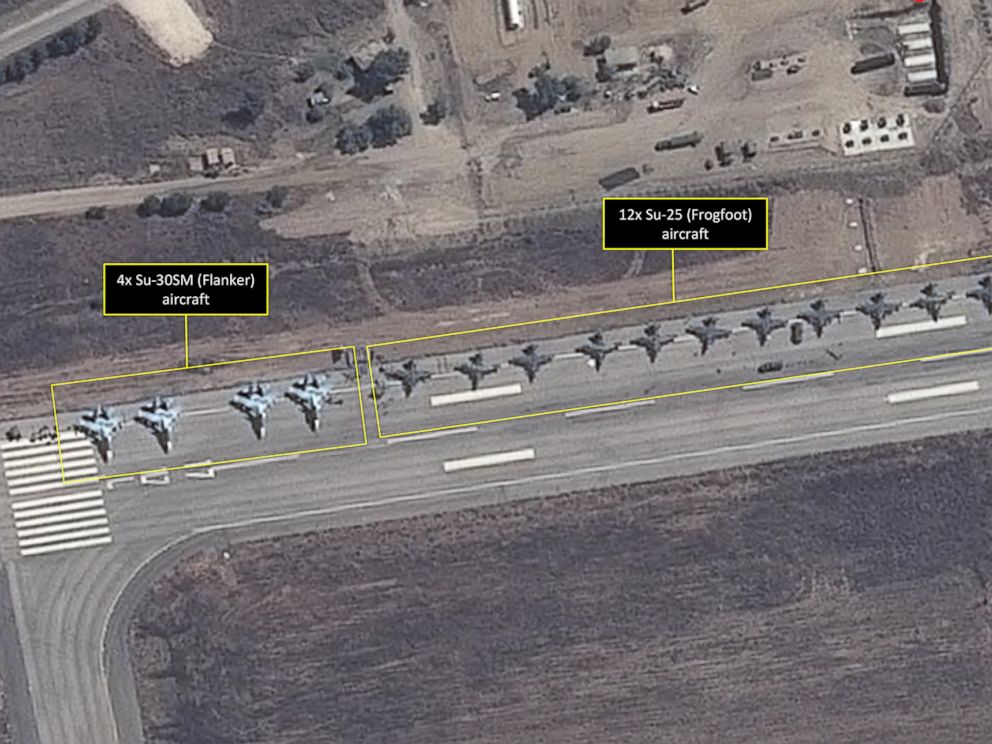 RUSSIAN AIR BASE (SYRIA)
RUSSIAN AIR BASE (SYRIA) AL-FATAH’S COAT OF ARMS
AL-FATAH’S COAT OF ARMS RUSSIAN BOMBERS HIT USA SPONSORED GROUND BASE IN SYRIA.
RUSSIAN BOMBERS HIT USA SPONSORED GROUND BASE IN SYRIA. PUTIN WILL HELP MADURO AGAINST BAKERIES’ MAFFIAS…
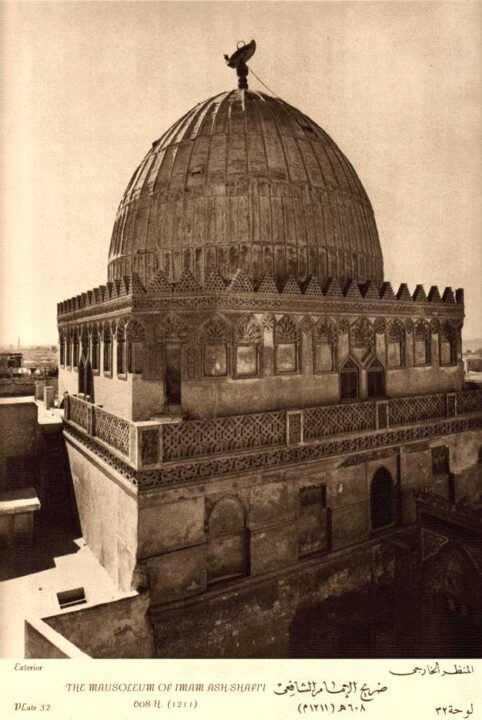
PUTIN WILL HELP MADURO AGAINST BAKERIES’ MAFFIAS… AL-SHAFII, LEADER OF ONE OF THE ISLAM’S IDEOLOGICAL SCHOOLS.
AL-SHAFII, LEADER OF ONE OF THE ISLAM’S IDEOLOGICAL SCHOOLS. THE «GREAT OR INNER MOSLEM JIHAD»…
THE «GREAT OR INNER MOSLEM JIHAD»… AL-AZHAR UNIVERSITY, CAIRO.
AL-AZHAR UNIVERSITY, CAIRO. AL-AZHAR’S RECTOR WITH TAWADROS II, THE 112th COPTIC PATRIARCH…
AL-AZHAR’S RECTOR WITH TAWADROS II, THE 112th COPTIC PATRIARCH…